This is a almost complete article for ELK stack implementation. However, the authorization restrictions in Kibana are a bit tricky, this article shows authorization at the webserver level for Apache (useful for smaller companies, for fine-grained permissions this might not be useful) i.e This article would serve the purpose of installing the above mentioned software stack. If later I come across anything different or useful when it comes to installing this article would be updated.
This is more like a step by step end to end tutorial, combining information from a lot of different sources. All the appropriate references are provided.
The actual log ingestion, monitoring etc… might be seperate articles.
This is for Ubuntu 20.04. I would suggest at least 4GB RAM. Based upon your requirements follow all or some of the steps
Steps:
- Update
2. Install Java
3. Install ElasticSearch
4. Minimal configuration of ElasticSearch
5. Attach a seperate data volume to EC2 instance in AWS (Optional)
6. Start and verify ElasticSearch
7. Installing Kibana
8. Installing NGinx (Optional if NGinx is installed)
9. Installing Apache and securing Apache (Optional if you have a different web server and secured in a different way)
9a) Securing using Auth0 (My preferred way due to some undisclosed reasons)
10. Install LetsEncrypt’s free SSL certificate for NGinx (Must, unless you have different form of SSL certificates)
11. Install LetsEncrypt’s free SSL certificate for Apache (Must, unless you have different form of SSL certificates)
12. Install Dex (Optional, configuring Dex is not covered in this article)
13. Configure Apache reverseproxy
14. Configure NGinx as a reverseproxy
- Update:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade2. Install Java
sudo apt install default-jre3. Install ElasticSearch
curl -fsSL https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch |sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/elastic.gpg
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/elastic.gpg] https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-7.x.list
sudo apt update
sudo apt install elasticsearch4. Minimal configuration of ElasticSearch
ElasticSearch stores configuration in a file located at /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml, for now we would uncomment network.host and set to localhost.
sudo nano /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
// uncomment network.host as shown below, press ctrl + x, Y + Enter i.e save the file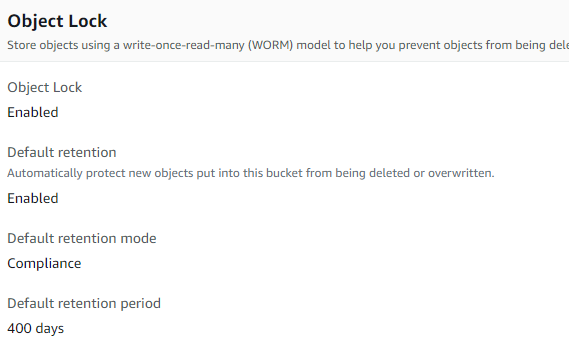
5. Attach a seperate data volume to EC2 instance in AWS (Optional)
Goto AWS Console, EC2 and click Volumes.
Then click Create Volume in the top right.
Select the appropriate volume type, size etc… and create volume

Once the volume is created and available, select the volume and click “Attach Volume” from the “Actions” menu.

Select the instance for which the volume needs to be attached and click attach.

Now SSH into the EC2 instance
lsblkThis should show something like this:

nvme1n1 was attached.
Format the newly attached volume
sudo mkfs -t xfs /dev/nvme1n1
Mount to /etc/lib/elasticsearch
sudo mount /dev/nvme1n1 /var/lib/elasticsearch/For the volume to be automatically mounted edit /etc/fstab. But prior, make a copy because it seems improper fstab configuration can cause problems.
sudo blkid
sudo nano /etc/fstabPaste the following line by replacing XXX with your own UUID from previous step.
UUID=XXX /var/lib/elasticsearch xfs defaults,nofail 0 26. Start and verify ElasticSearch
sudo systemctl start elasticsearch
sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch
curl -X GET "localhost:9200"
If the above 3 commands ran without error and if the output of 3rd command matches the above, elasticsearch installation is complete.
7. Installing Kibana
sudo apt install kibana
sudo systemctl enable kibana
sudo systemctl start kibana8. Installing NGinx (Optional if NGinx is installed)
sudo apt install nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginx
sudo systemctl start nginxEnable port 80 in Security Group, in firewall (ufw) if you have and navigate to the public IP address of your computer and see if the NGinx page is displayed.

9. Installing Apache and securing Apache (Optional if you have a different web server and secured in a different way)
sudo apt install apache2
sudo apt-get install libapache2-mod-auth-openidc
sudo a2enmod auth_openidcThe next steps are optional, these steps are for securing the website at the server level i.e as a one person company, for now, I need to secure websites directly at the server level. If access rights are an issue, those need to be handled at the application level.
/etc/apache2/sites-available
cp 000-default.conf kibana.conf
sudo nano kibana.confuncomment the ServerName line and use your own domain.

sudo a2ensite kibana.conf //Enabling the new conf
sudo a2dissite 000-default.conf //Disabling the old conf
sudo apache2ctl configtest //Validate syntax
sudo systemctl restart apache2 //Restart ApacheInstall SSL cert as mentioned in 11 and then proceed.
Install Apache OpenID Connect and secure
sudo apt install libapache2-mod-auth-openidcCreate a new app in Google Console and then follow these instructions. Here are the instructions: https://support.google.com/cloud/answer/6158849?hl=en
Modify the appropriate Apache .conf file for your choosen provider. Here is a sample for Google login.
<VirtualHost>
...
OIDCClaimPrefix "OIDC-"
OIDCResponseType "code"
OIDCScope "openid email profile"
OIDCProviderMetadataURL https://accounts.google.com/.well-known/openid-configuration
OIDCClientID <YourClientID>
OIDCClientSecret <YourClientSecret>
OIDCCryptoPassphrase <StrongCryptoPhrase>
OIDCRedirectURI https://kibana.alightservices.com/v1/openid/callback
#The above URL can be any vanity URL
<LocationMatch />
AuthType openid-connect
Require valid-user
Require claim
LogLevel debug
</LocationMatch>
...
</VirtualHost>9a) Securing using Auth0 (My preferred way due to some undisclosed reasons)
OIDCClaimPrefix "OIDC-"
OIDCResponseType "code"
OIDCScope "openid email profile"
OIDCProviderMetadataURL https://alightservices.eu.auth0.com/.well-known/openid-configuration
OIDCClientID <YourCLientId>
OIDCClientSecret <YourClientSecret>10. Install LetsEncrypt’s free SSL certificate for NGinx (Must, unless you have different form of SSL certificates)
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginxEdit the nginx config file, here I am editing the default file:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/Add the following in the server block
server_name kibana.alightservices.com;
Verify and restart nginx
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginxGenerate certificates by issuing the following command and following the instructions:
sudo certbot --nginx11. Install LetsEncrypt’s free SSL certificate for Apache (Must, unless you have different form of SSL certificates)
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-apache
sudo certbot --apache12. Install Dex (Optional, configuring Dex is not covered in this article)
Dex needs go, gcc and build-essentials
sudo apt install make gcc build-essentials
curl https://go.dev/dl/go1.19.4.linux-amd64.tar.gz
rm -rf /usr/local/go && tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.19.4.linux-amd64.tar.gz
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin
git clone https://github.com/dexidp/dex.git
cd dex/
make build13. Configure Apache reverseproxy
Enable the following modules:
sudo a2enmod proxy
sudo a2enmod proxy_http
sudo a2enmod proxy_balancer
sudo a2enmod lbmethod_byrequestsIn the appropriate .conf file remove “DocumentRoot” and add these lines:
ProxyPass / http://127.0.0.1:5601/
ProxyPassReverse / http://127.0.0.1:5601/The validate the config file and restart apache
apachectl configtest
sudo systemctl restart apache214. Configure NGinx as a reverseproxy
Inside your nginx config file inside “server” block, configure “location” block to look like this:
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5601;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade';
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}Restart nginx
sudo systemctl rsetart nginxThat’s all voila ElasticSearch and Kibana are up and running! Injecting logs configurations etc… are the topics for another blog post.
References
Apache OpenID Connect example. (n.d.). Retrieved January 2, 2023, from https://docs.openathens.net/providers/apache-openid-connect-example
Boucheron, B. (2021, March 1). How To Secure Nginx with Let's Encrypt on Ubuntu 20.04. DigitalOcean Community. Retrieved January 2, 2023, from https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-secure-nginx-with-let-s-encrypt-on-ubuntu-20-04
Glass, E., & Camisso, J. (2022, April 26). How To Install Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana (Elastic Stack) on Ubuntu 22.04. DigitalOcean Community. Retrieved January 2, 2023, from https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-install-elasticsearch-logstash-and-kibana-elastic-stack-on-ubuntu-22-04
Heidi, E. (2020, April 29). How To Secure Apache with Let's Encrypt on Ubuntu 20.04. DigitalOcean Community. Retrieved January 2, 2023, from https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-secure-apache-with-let-s-encrypt-on-ubuntu-20-04
Krantz, X. (2021, December 14). How to setup SSO for Elastic/Kibana with GitHub auth provider. Medium. https://medium.com/devobs/how-to-setup-sso-for-elastic-kibana-with-github-auth-provider-7268128977f9
Make an Amazon EBS volume available for use on Linux – Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud. (n.d.). AWS Documentation. Retrieved January 1, 2023, from https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/ebs-using-volumes.html
OpenStack Docs: Setup OpenID Connect. (n.d.). Retrieved January 2, 2023, from https://docs.openstack.org/keystone/pike/advanced-topics/federation/openidc.html
ZmartZone IAM. (n.d.-a). GitHub – zmartzone/mod_auth_openidc: OpenID Certified<sup>TM OpenID Connect Relying Party implementation for Apache HTTP Server 2.x. GitHub. Retrieved January 2, 2023, from <span>https://github.com/zmartzone/mod_auth_openidc
ZmartZone IAM. (n.d.-b). Home · zmartzone/mod_auth_openidc Wiki. GitHub. Retrieved January 2, 2023, from https://github.com/zmartzone/mod_auth_openidc/wiki